Vector Mathematics: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
This guide covers... Mostrar más
Asignaturas
Comunicación Académica Escrita
Modos y Estructuras Verbales
Literatura Medieval Española
Movimientos Literarios Hispanoamericanos
Herencia Lingüística Latina
Figuras Retóricas y Literarias
Generación del 98: Crisis y Renovación
Grandes Autores Hispánicos Modernos
Conceptos de Género
Teatro Español Trágico
Mostrar todos los temas
Reformas Políticas en España 1812-1874
El Renacimiento y la Ilustración Europea
La Revolución Francesa y el Absolutismo 1750-1799
Las Guerras Religiosas Medievales
La Era Napoleónica 1803-1830
La Civilización Romana Antigua
El Darwinismo Social y el Imperialismo
Conflictos Militares Modernos
Las Revoluciones Industriales y Tecnológicas
Migraciones e Invasiones Medievales
Mostrar todos los temas
Estructura y Organización Biomolecular
Sistemas de Órganos Humanos
Tipos de Organización Celular
Tipos de Tejidos Biológicos
Metabolismo Energético y Nutrición
Organización y Desarrollo Celular
Ciencias Básicas de la Vida
Subdisciplinas de las Ciencias Biológicas
Sistemas Ecológicos e Interacciones
Ciclos de Células Reproductivas
Mostrar todos los temas
Propiedades de Exponentes y Logaritmos
Operaciones y Transformaciones Matriciales
Operaciones y Métodos de División
Expresiones Racionales y Radicales
Clasificación de los Números Reales
Operaciones con Expresiones Racionales
Operaciones con Notación Decimal y Científica
Límites de Funciones y Asíntotas
Sustracción y Números Negativos
Propiedades y Clasificación de Triángulos
Mostrar todos los temas
Orígenes de la Filosofía Griega Antigua
Subdisciplinas y Enfoques Filosóficos
Métodos de Adquisición del Conocimiento
Mitos Filosóficos Griegos
Metafísica Aristotélica
Movimientos Filosóficos Modernos
Filosofía Cristiana Medieval
Dualismo Mente-Cuerpo
Filósofos Occidentales Modernos
Métodos de Argumentación Lógica
Mostrar todos los temas
157
•
28 ene 2026
•
Vector Mathematics: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
This guide covers... Mostrar más




This page delves deeper into vector operations and introduces the concept of vector bases, which is essential for understanding vector mathematics in higher dimensions.
The page covers:
Definition: A vector base is a set of linearly independent vectors that can be used to represent any vector in the space.
The page provides examples of vector bases and introduces the canonical basis, which is fundamental in vector algebra.
Example: In 2D space, the canonical basis consists of vectors i = (1,0) and j = (0,1).
The concept of orthogonal and orthonormal bases is introduced, which is crucial for understanding more advanced topics in vector algebra.
Highlight: Orthonormal bases, such as the canonical basis, simplify many calculations in vector mathematics.
The page also covers the properties of vector operations, including:
These concepts are essential for students learning about vector operations and preparing for more advanced topics in linear algebra.

This page focuses on the dot product (scalar product) of vectors and its applications, including vector projections and angle calculations. These concepts are crucial for students studying product escalar de dos vectores (dot product of two vectors).
The page covers:
Formula: The dot product of two vectors a and b is given by a · b = |a| |b| cos(θ), where θ is the angle between the vectors.
The page explains how to use the dot product to determine if vectors are perpendicular:
Highlight: If the dot product of two vectors is zero, they are perpendicular (orthogonal) to each other.
Vector projections are introduced, which are important applications of the dot product:
Definition: The projection of a vector v onto a vector u is given by the formula: proj_u v = u
The page emphasizes the importance of these concepts in various fields of mathematics and physics, making it essential for students studying vectores 1 bachillerato ejercicios resueltos (vector exercises for high school students).

This final page covers the vector product (cross product) and its applications, including area and volume calculations. It also introduces the concept of the scalar triple product, which is important for students studying advanced vector mathematics.
The page covers:
Formula: The magnitude of the vector product |a × b| = |a| |b| sin(θ) represents the area of the parallelogram formed by the two vectors.
The page provides a step-by-step guide for solving problems involving the vector product:
Example: The volume of a tetrahedron can be calculated using the scalar triple product: V = (1/6)|a · (b × c)|, where a, b, and c are vectors representing three edges of the tetrahedron.
The page concludes with a discussion on coplanar vectors and the use of determinants in vector calculations, which is crucial for students studying multiplicación de vectores ejercicios resueltos (vector multiplication solved exercises).
Highlight: The scalar triple product or vector product equaling zero indicates that the vectors are coplanar (lie in the same plane).
This comprehensive guide provides students with a solid foundation in vector mathematics, preparing them for advanced topics in linear algebra and multivariable calculus.

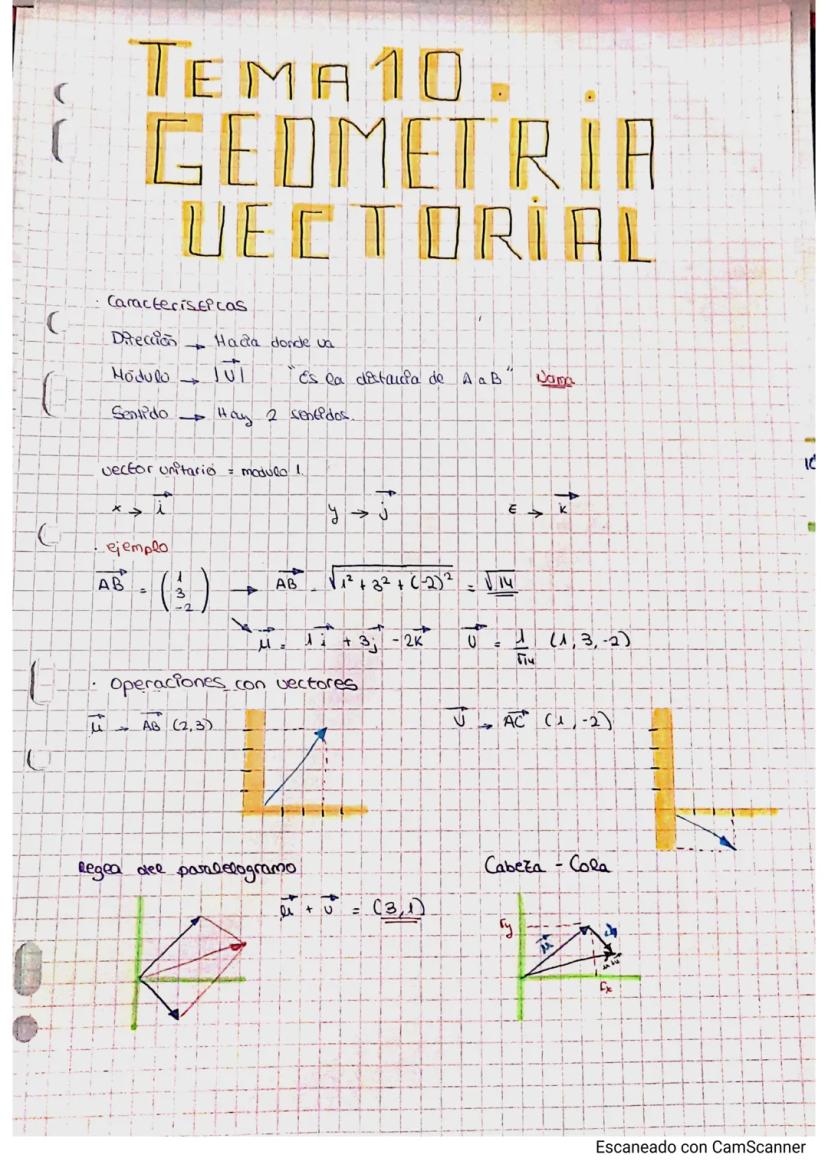
This page introduces the fundamental concepts of vectors in mathematics. It covers the basic properties and operations of vectors, essential for students studying vector mathematics.
Definition: A vector is a mathematical object with both magnitude and direction.
The page explains the key characteristics of vectors:
Example: A vector AB (2,3) represents a displacement of 2 units in the x-direction and 3 units in the y-direction.
The page also introduces vector operations, including:
Vocabulary: Unit vector - A vector with a magnitude of 1, often used to represent direction.
Students are introduced to the concept of vector representation in coordinate systems, which is crucial for solving problems in vector mathematics.
Nuestro compañero de IA está específicamente adaptado a las necesidades de los estudiantes. Basándonos en los millones de contenidos que tenemos en la plataforma, podemos dar a los estudiantes respuestas realmente significativas y relevantes. Pero no se trata solo de respuestas, el compañero también guía a los estudiantes a través de sus retos de aprendizaje diarios, con planes de aprendizaje personalizados, cuestionarios o contenidos en el chat y una personalización del 100% basada en las habilidades y el desarrollo de los estudiantes.
Puedes descargar la app en Google Play Store y Apple App Store.
Sí, tienes acceso gratuito a los contenidos de la aplicación y a nuestro compañero de IA. Para desbloquear determinadas funciones de la aplicación, puedes adquirir Knowunity Pro.
App Store
Google Play
La app es muy fácil de usar y está muy bien diseñada. Hasta ahora he encontrado todo lo que estaba buscando y he podido aprender mucho de las presentaciones. Definitivamente utilizaré la aplicación para un examen de clase. Y, por supuesto, también me sirve mucho de inspiración.
Pablo
usuario de iOS
Esta app es realmente genial. Hay tantos apuntes de clase y ayuda [...]. Tengo problemas con matemáticas, por ejemplo, y la aplicación tiene muchas opciones de ayuda. Gracias a Knowunity, he mejorado en mates. Se la recomiendo a todo el mundo.
Elena
usuaria de Android
Vaya, estoy realmente sorprendida. Acabo de probar la app porque la he visto anunciada muchas veces y me he quedado absolutamente alucinada. Esta app es LA AYUDA que quieres para el insti y, sobre todo, ofrece muchísimas cosas, como ejercicios y hojas informativas, que a mí personalmente me han sido MUY útiles.
Ana
usuaria de iOS
Está app es muy buena, tiene apuntes que son de mucha ayuda y su IA es fantástica, te explica a la perfección y muy fácil de entender lo que necesites, te ayuda con los deberes, te hace esquemas... en definitiva es una muy buena opción!
Sophia
usuario de Android
Me encanta!!! Me resuelve todo con detalle y me da la explicación correcta. Tiene un montón de funciones, ami me ha ido genial!! Os la recomiendo!!!
Marta
usuaria de Android
La uso casi diariamente, sirve para todas las asignaturas. Yo, por ejemplo la utilizo más en inglés porque se me da bastante mal, ¡Todas las respuestas están correctas! Consta con personas reales que suben sus apuntes y IA para que puedas hacer los deberes muchísimo más fácil, la recomiendo.
Izan
usuario de iOS
¡La app es buenísima! Sólo tengo que introducir el tema en la barra de búsqueda y recibo la respuesta muy rápido. No tengo que ver 10 vídeos de YouTube para entender algo, así que me ahorro tiempo. ¡Muy recomendable!
Sara
usuaria de Android
En el instituto era muy malo en matemáticas, pero gracias a la app, ahora saco mejores notas. Os agradezco mucho que hayáis creado la aplicación.
Roberto
usuario de Android
Esto no es como Chatgpt, es MUCHISMO MEJOR, te hace unos resúmenes espectaculares y gracias a esta app pase de sacar 5-6 a sacar 8-9.
Julyana
usuaria de Android
Es la mejor aplicación del mundo, la uso para revisar los deberes a mi hijo.
Javier
usuario de Android
LOS QUIZ Y FLASHCARDS SON SÚPER ÚTILES Y ME ENCANTA Knowunity IA. ADEMÁS ES LITERALMENTE COMO CHATGPT PERO MÁS LISTO!! ME AYUDÓ TAMBIÉN CON MIS PROBLEMAS DE MÁSCARA!! Y CON MIS ASIGNATURAS DE VERDAD! OBVIO 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Erick
usuario de Android
Me me encanta esta app, todo lo que tiene es de calidad ya que antes de ser publicado es revisado por un equipo de profesionales. Me ha ido genial esta aplicación ya que gracias a ella puedo estudiar mucho mejor, sin tener que agobiarme porque mi profesor no ha hecho teoría o porque no entiendo su teoría. Le doy un 10 de 10!
Mar
usuaria de iOS
La app es muy fácil de usar y está muy bien diseñada. Hasta ahora he encontrado todo lo que estaba buscando y he podido aprender mucho de las presentaciones. Definitivamente utilizaré la aplicación para un examen de clase. Y, por supuesto, también me sirve mucho de inspiración.
Pablo
usuario de iOS
Esta app es realmente genial. Hay tantos apuntes de clase y ayuda [...]. Tengo problemas con matemáticas, por ejemplo, y la aplicación tiene muchas opciones de ayuda. Gracias a Knowunity, he mejorado en mates. Se la recomiendo a todo el mundo.
Elena
usuaria de Android
Vaya, estoy realmente sorprendida. Acabo de probar la app porque la he visto anunciada muchas veces y me he quedado absolutamente alucinada. Esta app es LA AYUDA que quieres para el insti y, sobre todo, ofrece muchísimas cosas, como ejercicios y hojas informativas, que a mí personalmente me han sido MUY útiles.
Ana
usuaria de iOS
Está app es muy buena, tiene apuntes que son de mucha ayuda y su IA es fantástica, te explica a la perfección y muy fácil de entender lo que necesites, te ayuda con los deberes, te hace esquemas... en definitiva es una muy buena opción!
Sophia
usuario de Android
Me encanta!!! Me resuelve todo con detalle y me da la explicación correcta. Tiene un montón de funciones, ami me ha ido genial!! Os la recomiendo!!!
Marta
usuaria de Android
La uso casi diariamente, sirve para todas las asignaturas. Yo, por ejemplo la utilizo más en inglés porque se me da bastante mal, ¡Todas las respuestas están correctas! Consta con personas reales que suben sus apuntes y IA para que puedas hacer los deberes muchísimo más fácil, la recomiendo.
Izan
usuario de iOS
¡La app es buenísima! Sólo tengo que introducir el tema en la barra de búsqueda y recibo la respuesta muy rápido. No tengo que ver 10 vídeos de YouTube para entender algo, así que me ahorro tiempo. ¡Muy recomendable!
Sara
usuaria de Android
En el instituto era muy malo en matemáticas, pero gracias a la app, ahora saco mejores notas. Os agradezco mucho que hayáis creado la aplicación.
Roberto
usuario de Android
Esto no es como Chatgpt, es MUCHISMO MEJOR, te hace unos resúmenes espectaculares y gracias a esta app pase de sacar 5-6 a sacar 8-9.
Julyana
usuaria de Android
Es la mejor aplicación del mundo, la uso para revisar los deberes a mi hijo.
Javier
usuario de Android
LOS QUIZ Y FLASHCARDS SON SÚPER ÚTILES Y ME ENCANTA Knowunity IA. ADEMÁS ES LITERALMENTE COMO CHATGPT PERO MÁS LISTO!! ME AYUDÓ TAMBIÉN CON MIS PROBLEMAS DE MÁSCARA!! Y CON MIS ASIGNATURAS DE VERDAD! OBVIO 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Erick
usuario de Android
Me me encanta esta app, todo lo que tiene es de calidad ya que antes de ser publicado es revisado por un equipo de profesionales. Me ha ido genial esta aplicación ya que gracias a ella puedo estudiar mucho mejor, sin tener que agobiarme porque mi profesor no ha hecho teoría o porque no entiendo su teoría. Le doy un 10 de 10!
Mar
usuaria de iOS
Vector Mathematics: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
This guide covers essential concepts in vector mathematics, including vector operations, scalar multiplication, dot product, and geometric interpretations. It's designed for high school and early university students studying vectors.
Key topics:

Acceso a todos los documentos
Mejora tus notas
Únete a millones de estudiantes
Al registrarte aceptas las Condiciones del servicio y la Política de privacidad.
This page delves deeper into vector operations and introduces the concept of vector bases, which is essential for understanding vector mathematics in higher dimensions.
The page covers:
Definition: A vector base is a set of linearly independent vectors that can be used to represent any vector in the space.
The page provides examples of vector bases and introduces the canonical basis, which is fundamental in vector algebra.
Example: In 2D space, the canonical basis consists of vectors i = (1,0) and j = (0,1).
The concept of orthogonal and orthonormal bases is introduced, which is crucial for understanding more advanced topics in vector algebra.
Highlight: Orthonormal bases, such as the canonical basis, simplify many calculations in vector mathematics.
The page also covers the properties of vector operations, including:
These concepts are essential for students learning about vector operations and preparing for more advanced topics in linear algebra.

Acceso a todos los documentos
Mejora tus notas
Únete a millones de estudiantes
Al registrarte aceptas las Condiciones del servicio y la Política de privacidad.
This page focuses on the dot product (scalar product) of vectors and its applications, including vector projections and angle calculations. These concepts are crucial for students studying product escalar de dos vectores (dot product of two vectors).
The page covers:
Formula: The dot product of two vectors a and b is given by a · b = |a| |b| cos(θ), where θ is the angle between the vectors.
The page explains how to use the dot product to determine if vectors are perpendicular:
Highlight: If the dot product of two vectors is zero, they are perpendicular (orthogonal) to each other.
Vector projections are introduced, which are important applications of the dot product:
Definition: The projection of a vector v onto a vector u is given by the formula: proj_u v = u
The page emphasizes the importance of these concepts in various fields of mathematics and physics, making it essential for students studying vectores 1 bachillerato ejercicios resueltos (vector exercises for high school students).

Acceso a todos los documentos
Mejora tus notas
Únete a millones de estudiantes
Al registrarte aceptas las Condiciones del servicio y la Política de privacidad.
This final page covers the vector product (cross product) and its applications, including area and volume calculations. It also introduces the concept of the scalar triple product, which is important for students studying advanced vector mathematics.
The page covers:
Formula: The magnitude of the vector product |a × b| = |a| |b| sin(θ) represents the area of the parallelogram formed by the two vectors.
The page provides a step-by-step guide for solving problems involving the vector product:
Example: The volume of a tetrahedron can be calculated using the scalar triple product: V = (1/6)|a · (b × c)|, where a, b, and c are vectors representing three edges of the tetrahedron.
The page concludes with a discussion on coplanar vectors and the use of determinants in vector calculations, which is crucial for students studying multiplicación de vectores ejercicios resueltos (vector multiplication solved exercises).
Highlight: The scalar triple product or vector product equaling zero indicates that the vectors are coplanar (lie in the same plane).
This comprehensive guide provides students with a solid foundation in vector mathematics, preparing them for advanced topics in linear algebra and multivariable calculus.

Acceso a todos los documentos
Mejora tus notas
Únete a millones de estudiantes
Al registrarte aceptas las Condiciones del servicio y la Política de privacidad.
This page introduces the fundamental concepts of vectors in mathematics. It covers the basic properties and operations of vectors, essential for students studying vector mathematics.
Definition: A vector is a mathematical object with both magnitude and direction.
The page explains the key characteristics of vectors:
Example: A vector AB (2,3) represents a displacement of 2 units in the x-direction and 3 units in the y-direction.
The page also introduces vector operations, including:
Vocabulary: Unit vector - A vector with a magnitude of 1, often used to represent direction.
Students are introduced to the concept of vector representation in coordinate systems, which is crucial for solving problems in vector mathematics.
Nuestro compañero de IA está específicamente adaptado a las necesidades de los estudiantes. Basándonos en los millones de contenidos que tenemos en la plataforma, podemos dar a los estudiantes respuestas realmente significativas y relevantes. Pero no se trata solo de respuestas, el compañero también guía a los estudiantes a través de sus retos de aprendizaje diarios, con planes de aprendizaje personalizados, cuestionarios o contenidos en el chat y una personalización del 100% basada en las habilidades y el desarrollo de los estudiantes.
Puedes descargar la app en Google Play Store y Apple App Store.
Sí, tienes acceso gratuito a los contenidos de la aplicación y a nuestro compañero de IA. Para desbloquear determinadas funciones de la aplicación, puedes adquirir Knowunity Pro.
3
Herramientas Inteligentes NUEVO
Transforma estos apuntes en: ✓ 50+ Preguntas de Práctica ✓ Flashcards Interactivas ✓ Examen Completo de Práctica ✓ Esquemas de Ensayo
Teoría tema vectores (bloque geometría)
Explicación y ejercicios de geometría en el espacio en relación con rectas y planos
Apuntes
Apuntes del tema de vectores
Explicación y ejercicios de vectores.
Apuntes
App Store
Google Play
La app es muy fácil de usar y está muy bien diseñada. Hasta ahora he encontrado todo lo que estaba buscando y he podido aprender mucho de las presentaciones. Definitivamente utilizaré la aplicación para un examen de clase. Y, por supuesto, también me sirve mucho de inspiración.
Pablo
usuario de iOS
Esta app es realmente genial. Hay tantos apuntes de clase y ayuda [...]. Tengo problemas con matemáticas, por ejemplo, y la aplicación tiene muchas opciones de ayuda. Gracias a Knowunity, he mejorado en mates. Se la recomiendo a todo el mundo.
Elena
usuaria de Android
Vaya, estoy realmente sorprendida. Acabo de probar la app porque la he visto anunciada muchas veces y me he quedado absolutamente alucinada. Esta app es LA AYUDA que quieres para el insti y, sobre todo, ofrece muchísimas cosas, como ejercicios y hojas informativas, que a mí personalmente me han sido MUY útiles.
Ana
usuaria de iOS
Está app es muy buena, tiene apuntes que son de mucha ayuda y su IA es fantástica, te explica a la perfección y muy fácil de entender lo que necesites, te ayuda con los deberes, te hace esquemas... en definitiva es una muy buena opción!
Sophia
usuario de Android
Me encanta!!! Me resuelve todo con detalle y me da la explicación correcta. Tiene un montón de funciones, ami me ha ido genial!! Os la recomiendo!!!
Marta
usuaria de Android
La uso casi diariamente, sirve para todas las asignaturas. Yo, por ejemplo la utilizo más en inglés porque se me da bastante mal, ¡Todas las respuestas están correctas! Consta con personas reales que suben sus apuntes y IA para que puedas hacer los deberes muchísimo más fácil, la recomiendo.
Izan
usuario de iOS
¡La app es buenísima! Sólo tengo que introducir el tema en la barra de búsqueda y recibo la respuesta muy rápido. No tengo que ver 10 vídeos de YouTube para entender algo, así que me ahorro tiempo. ¡Muy recomendable!
Sara
usuaria de Android
En el instituto era muy malo en matemáticas, pero gracias a la app, ahora saco mejores notas. Os agradezco mucho que hayáis creado la aplicación.
Roberto
usuario de Android
Esto no es como Chatgpt, es MUCHISMO MEJOR, te hace unos resúmenes espectaculares y gracias a esta app pase de sacar 5-6 a sacar 8-9.
Julyana
usuaria de Android
Es la mejor aplicación del mundo, la uso para revisar los deberes a mi hijo.
Javier
usuario de Android
LOS QUIZ Y FLASHCARDS SON SÚPER ÚTILES Y ME ENCANTA Knowunity IA. ADEMÁS ES LITERALMENTE COMO CHATGPT PERO MÁS LISTO!! ME AYUDÓ TAMBIÉN CON MIS PROBLEMAS DE MÁSCARA!! Y CON MIS ASIGNATURAS DE VERDAD! OBVIO 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Erick
usuario de Android
Me me encanta esta app, todo lo que tiene es de calidad ya que antes de ser publicado es revisado por un equipo de profesionales. Me ha ido genial esta aplicación ya que gracias a ella puedo estudiar mucho mejor, sin tener que agobiarme porque mi profesor no ha hecho teoría o porque no entiendo su teoría. Le doy un 10 de 10!
Mar
usuaria de iOS
La app es muy fácil de usar y está muy bien diseñada. Hasta ahora he encontrado todo lo que estaba buscando y he podido aprender mucho de las presentaciones. Definitivamente utilizaré la aplicación para un examen de clase. Y, por supuesto, también me sirve mucho de inspiración.
Pablo
usuario de iOS
Esta app es realmente genial. Hay tantos apuntes de clase y ayuda [...]. Tengo problemas con matemáticas, por ejemplo, y la aplicación tiene muchas opciones de ayuda. Gracias a Knowunity, he mejorado en mates. Se la recomiendo a todo el mundo.
Elena
usuaria de Android
Vaya, estoy realmente sorprendida. Acabo de probar la app porque la he visto anunciada muchas veces y me he quedado absolutamente alucinada. Esta app es LA AYUDA que quieres para el insti y, sobre todo, ofrece muchísimas cosas, como ejercicios y hojas informativas, que a mí personalmente me han sido MUY útiles.
Ana
usuaria de iOS
Está app es muy buena, tiene apuntes que son de mucha ayuda y su IA es fantástica, te explica a la perfección y muy fácil de entender lo que necesites, te ayuda con los deberes, te hace esquemas... en definitiva es una muy buena opción!
Sophia
usuario de Android
Me encanta!!! Me resuelve todo con detalle y me da la explicación correcta. Tiene un montón de funciones, ami me ha ido genial!! Os la recomiendo!!!
Marta
usuaria de Android
La uso casi diariamente, sirve para todas las asignaturas. Yo, por ejemplo la utilizo más en inglés porque se me da bastante mal, ¡Todas las respuestas están correctas! Consta con personas reales que suben sus apuntes y IA para que puedas hacer los deberes muchísimo más fácil, la recomiendo.
Izan
usuario de iOS
¡La app es buenísima! Sólo tengo que introducir el tema en la barra de búsqueda y recibo la respuesta muy rápido. No tengo que ver 10 vídeos de YouTube para entender algo, así que me ahorro tiempo. ¡Muy recomendable!
Sara
usuaria de Android
En el instituto era muy malo en matemáticas, pero gracias a la app, ahora saco mejores notas. Os agradezco mucho que hayáis creado la aplicación.
Roberto
usuario de Android
Esto no es como Chatgpt, es MUCHISMO MEJOR, te hace unos resúmenes espectaculares y gracias a esta app pase de sacar 5-6 a sacar 8-9.
Julyana
usuaria de Android
Es la mejor aplicación del mundo, la uso para revisar los deberes a mi hijo.
Javier
usuario de Android
LOS QUIZ Y FLASHCARDS SON SÚPER ÚTILES Y ME ENCANTA Knowunity IA. ADEMÁS ES LITERALMENTE COMO CHATGPT PERO MÁS LISTO!! ME AYUDÓ TAMBIÉN CON MIS PROBLEMAS DE MÁSCARA!! Y CON MIS ASIGNATURAS DE VERDAD! OBVIO 😍😁😲🤑💗✨🎀😮
Erick
usuario de Android
Me me encanta esta app, todo lo que tiene es de calidad ya que antes de ser publicado es revisado por un equipo de profesionales. Me ha ido genial esta aplicación ya que gracias a ella puedo estudiar mucho mejor, sin tener que agobiarme porque mi profesor no ha hecho teoría o porque no entiendo su teoría. Le doy un 10 de 10!
Mar
usuaria de iOS